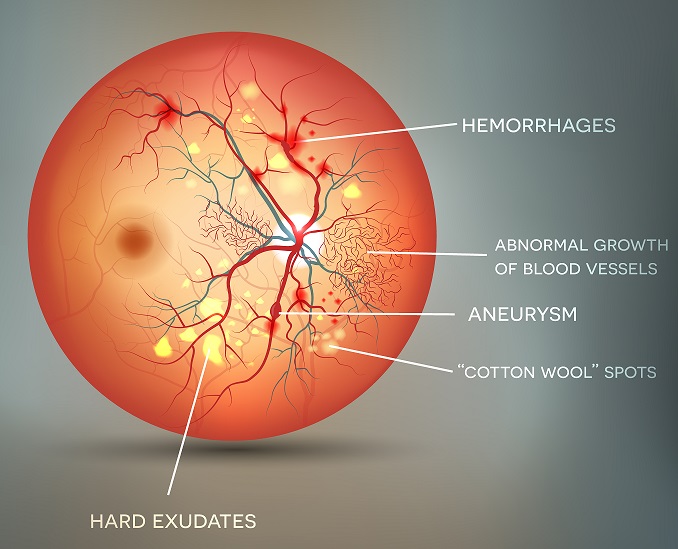
Diabetes serves as the most prominent reason for blindness for people under the age of 50 years in the world. Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) globally, amounts to 2.6% of causes for blindness. Regular screening is crucial for diabetes patients to ensure that DR is detected at early stages. DR detection traditionally involves a physician’s examination of retinal imaging for the shape and appearance of different types of lesions. The main issue involved with DR detection is the manual diagnosis process that is time, money and effort consuming since it involves an ophthalmologist’s examination of eye retinal fundus images, which also proves difficult particularly in the early stages of the disease when disease features are less prominent in the images. Medical image analysis has proven competency in assessing retinal fundus images and the utilization of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for deep learning (DL) in medical image analysis has aided the early diagnosis of DR.
This project is targeted at the utilization of state-of-the-art DL techniques to classify retinal fundus images and segment prominent regions aiming to reduce the resource consuming process of manual diagnosis and improve robustness of diagnsis by learning from big data.