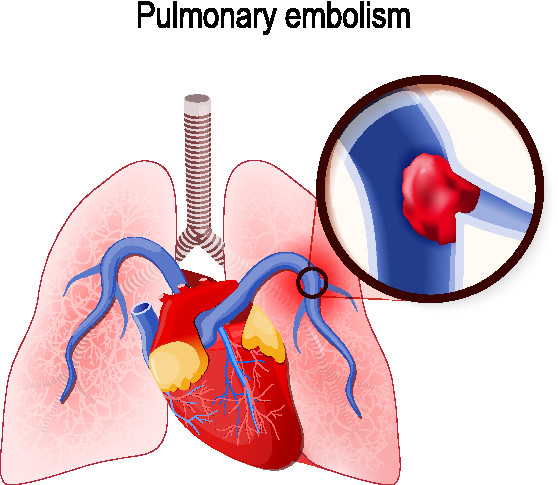
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a common pulmonary disease. It refers to a blockage in pulmonary arteries in the lung caused by blood clots. Such blood clots usually form in other areas of the body and travel to the lungs due to blood circulation. Patients with pulmonary embolism may collapse due to a shortage of oxygen-carrying blood in the affected areas of the lungs. In the US alone, over 60,000-100,000 deaths per year are caused by pulmonary embolism. Using CT scans for non-invasive diagnosis of the PE, clinicians have tended to over-diagnose PE to ensure the absence of PE rather than confirming PE in patients with chest-related symptoms. In addition, diagnosis involving CT scan examination is often time-consuming calling the need for a more robust solution.
Our goal is to develop an ML model to reliably and automatically diagnose and localize pulmonary embolism to aid clinicians to perform a rapid treatment plan.